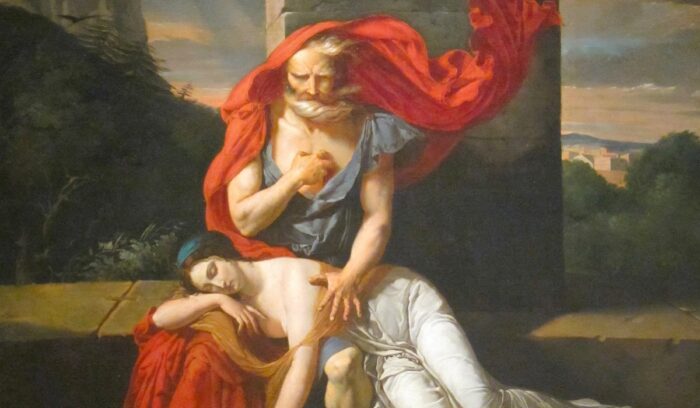
Sophocles completes the Oedipus trilogy of tragic plays
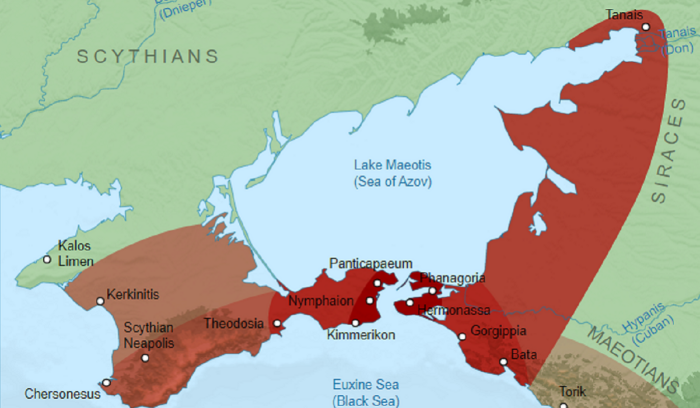
Sophocles (c. 496 – c. 406 B.C.E.) was one of the most famous and celebrated writers of tragedy plays in ancient Greece and his surviving works, written throughout the 5th century B.C.E., include such classics as Oedipus the King, Antigone, and Women of Trachis.