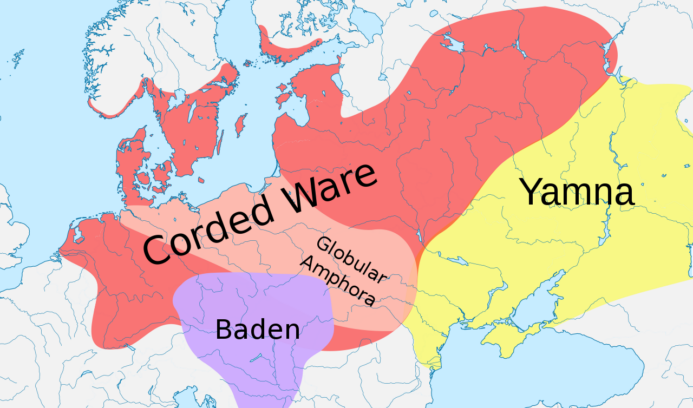
Ancient Egyptians begin using papyrus as a writing surface
Papyrus is first known to have been used in ancient Egypt (at least as far back as the First Dynasty), as the papyrus plant was once abundant across the Nile Delta. Apart from a writing material, ancient Egyptians employed papyrus in the construction of other artifacts, such as reed boats, mats, rope, sandals, and baskets.